Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
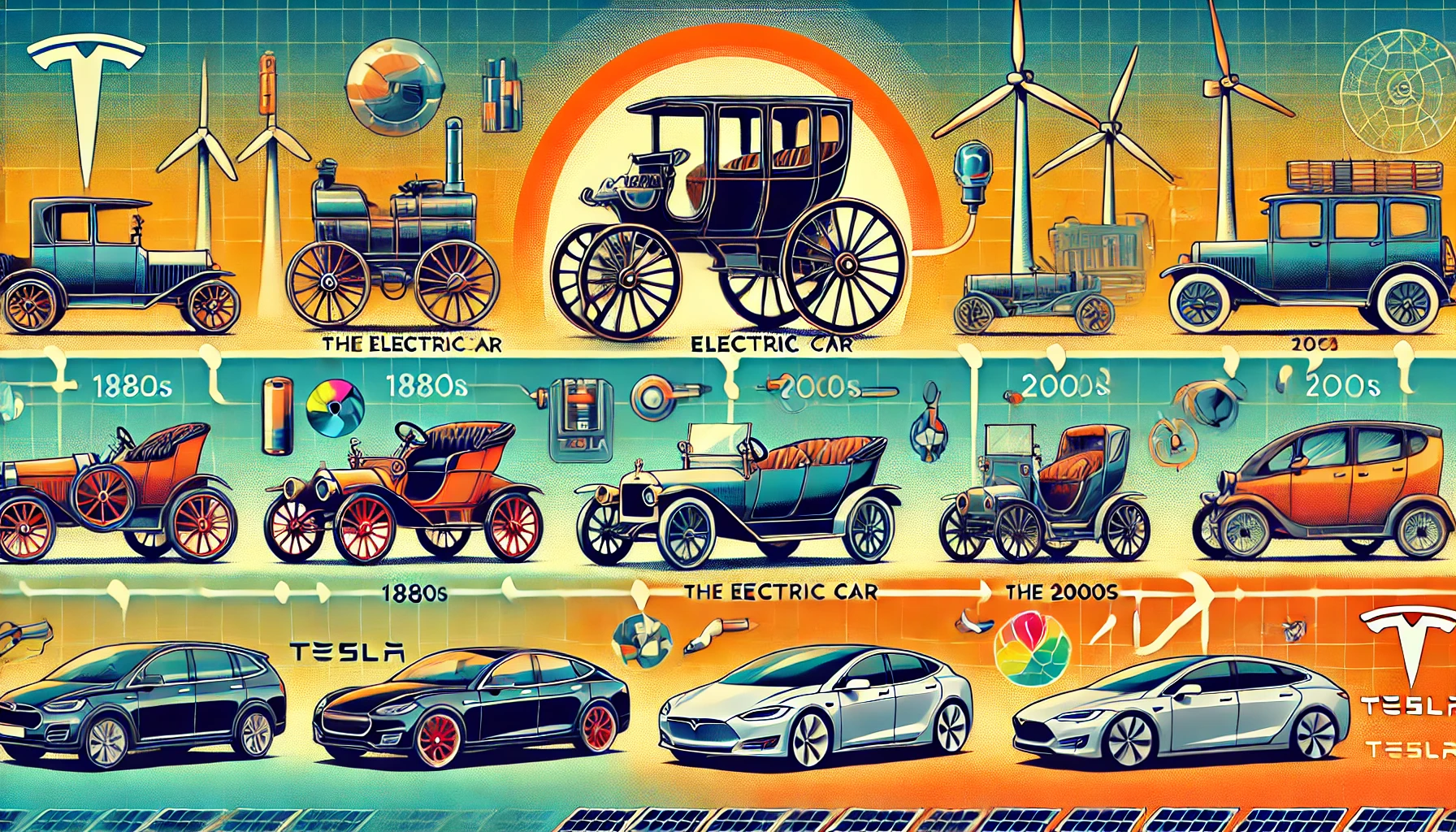

Electric cars (EVs) are redefining transportation, offering cleaner, more efficient alternatives to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. With advancements in battery technology and a surge in environmental consciousness, EVs have become a symbol of sustainable innovation. But the story of electric cars is not new—it dates back over 200 years.
The journey of electric cars began in the early 19th century. Inventors in Europe and the United States experimented with battery-powered carriages. Some key milestones include:
By the late 1800s, electric cars gained popularity for their quiet operation and ease of use compared to noisy, crank-start gasoline vehicles.
In the 1890s, electric cars flourished. They were especially favored in urban areas where gasoline cars were impractical due to limited fuel infrastructure and challenging manual gear shifts. Some notable developments include:
At this time, electric taxis operated in cities like New York and London, demonstrating the practicality of EVs.

Despite their early success, electric cars faced significant hurdles:
By the 1920s, electric cars had nearly vanished as internal combustion engines took over.
Between 1930 and 1960, interest in electric cars dwindled, but they never disappeared entirely. Small-scale attempts to revive them included vehicles like the Henney Kilowatt (1959), but these efforts were hampered by poor performance and lack of consumer interest.
The 1970s oil crisis reignited interest in electric vehicles:
During this period, companies developed experimental EVs, but technological limitations persisted.
The development of lithium-ion batteries in the 1990s revolutionized electric cars:
Governments worldwide have played a crucial role in the resurgence of electric cars:
Tesla, founded in 2003, revolutionized the electric car industry by combining luxury, performance, and sustainability. Key milestones include:
Tesla’s success inspired traditional automakers to invest heavily in electric cars.
The adoption of EVs varies by region:
The rise of electric cars has transformed the automotive industry:
While EVs reduce greenhouse gas emissions, challenges remain:
The future of EVs is promising:
Despite rapid growth, EVs face obstacles:
1. When was the first electric car invented?
The first practical electric car was built by William Morrison in 1891 in the U.S., though earlier experiments date back to the 1820s.
2. Why did electric cars lose popularity in the 1920s?
Gasoline cars became more affordable with the introduction of the Ford Model T, and better infrastructure supported their growth.
3. How did Tesla impact the EV market?
Tesla revolutionized EVs by proving they could be luxurious, high-performing, and sustainable.
4. What are the environmental benefits of electric cars?
They produce zero tailpipe emissions and reduce reliance on fossil fuels, helping to combat climate change.
5. What challenges do electric cars face today?
High costs, limited charging infrastructure, and raw material concerns are key challenges.
6. What is the future of electric vehicles?
Advancements in technology, growing government support, and consumer demand suggest a bright future for EVs.
The history of electric cars is a testament to human innovation and resilience. From humble beginnings to spearheading the green revolution, EVs are poised to dominate the future of transportation. As technology advances and challenges are overcome, electric cars will continue to drive us toward a sustainable tomorrow.